Education equity does not mean giving every student the exact same resources. Instead, it means providing each student with what they need to thrive, recognizing that some students face greater challenges than others. Inclusion ensures that all students, including those with disabilities, linguistic differences, and other unique needs, can fully participate in learning.
In this guide, we will explore:
- The difference between educational equity and equality.
- Barriers to equitable and inclusive education.
- Strategies for promoting fairness in schools.
- The role of technology in advancing educational equity.
- Global efforts to ensure inclusive education for all.
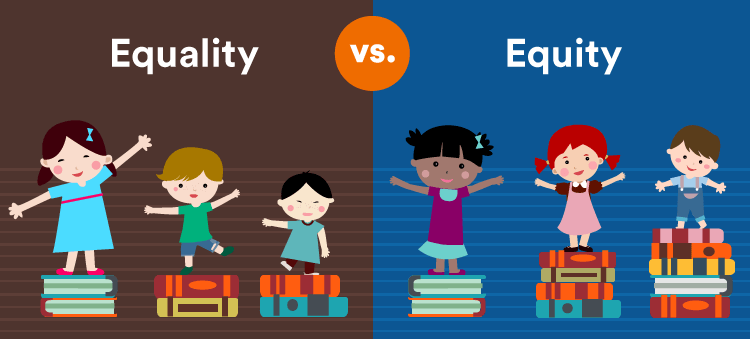
Educational Equity vs. Equality: What’s the Difference?

📌 Equality = Treating every student the same.
📌 Equity = Giving students what they need to succeed.
✅ Example of Equality: Every student receives the same textbook.
✅ Example of Equity: A student with a visual impairment receives a Braille or audio version of the textbook to ensure equal access to learning.
Equity focuses on fairness, while equality assumes that everyone has the same starting point.
Barriers to Educational Equity and Inclusion
1. Socioeconomic Disparities 💰
✔ Wealthier families can afford better schools, tutors, and technology, while low-income students may struggle with poorly funded schools and fewer resources.
✔ Solution: Invest in low-income schools, provide free school meals, and offer scholarships.
2. Racial and Ethnic Discrimination 🏫
✔ Minority students may experience bias in disciplinary actions, lower expectations from teachers, and limited access to advanced courses.
✔ Solution: Implement anti-bias training for educators, diverse curriculum representation, and policies ensuring fair discipline knowledge.
3. Gender Inequality 👩🎓👨🎓
✔ In many cultures, girls face barriers such as early marriage, lack of school safety, or limited encouragement in STEM fields.
✔ Solution: Provide scholarships for girls, encourage STEM education for all genders, and create safe school environments.
4. Support for those who needs
✔ Many students with physical or cognitive disabilities lack proper support, specialized teachers, or adaptive technology.
✔ Solution: Schools should adopt Universal Design for Learning (UDL), provide special education services, and integrate assistive technology.
5. Language Barriers 🌍
✔ Students who speak a language different from the primary language of instruction may struggle with comprehension.
✔ Solution: Implement bilingual education, hire multilingual teachers, and provide English as a Second Language (ESL) programs.
6. Geographic Disadvantages 🏞️
✔ Students in rural or remote areas may have limited access to quality teachers, internet, and learning resources.
✔ Solution: Expand online learning options, provide digital devices, and improve transportation services.
Strategies for Promoting Educational Equity and Inclusion
1. Culturally Responsive Teaching 🏫
- Use books, history, and examples from diverse cultures.
- Encourage students to share their backgrounds and learn from each other.
- Train teachers in anti-racism and inclusive education practices.
2. Universal Design for Learning (UDL) 📖
✔ Provides multiple ways of learning to accommodate different needs.
✔ Examples:
- Audio books for students with dyslexia.
- Hands-on experiments for kinesthetic learners.
📌 Example: Google Classroom and Microsoft’s Immersive Reader make learning more accessible.
3. Free and Affordable Educational Resources 💻
✔ Open-source textbooks, online courses, and free digital libraries help reduce financial barriers.
✔ Organizations like Khan Academy, Coursera, and OpenStax provide free high-quality education.
📌 Example: During COVID-19, UNESCO provided free online learning resources to millions of students worldwide.
4. Equity-Based School Funding 💰
✔ Schools in low-income areas should receive more funding and better resources.
✔ Adjust school funding models to prioritize schools with greater needs.
📌 Example: The U.S. Title I Program provides extra funding for schools with a high percentage of students from low-income families.
5. Inclusive Policies & Anti-Discrimination Laws 📜
✔ Governments must enforce policies that prohibit discrimination in education.
✔ Schools should adopt zero-tolerance policies for bullying and bias.
📌 Example: The Education for All initiative (EFA) by UNESCO promotes global education access.
The Role of Technology in Advancing Educational Equity
Technology can bridge educational gaps by making learning more accessible to marginalized students knowledge.
1. Online Learning Platforms 📱
✔ EdTech solutions like Zoom, Google Classroom, and Udemy help students learn remotely.
✔ Benefits students in rural areas, refugee camps, or low-income communities.
2. AI & Personalized Learning 🤖
✔ AI-driven platforms adjust lessons based on student progress, offering personalized learning experiences.
✔ Helps students struggling in specific subjects by providing tailored exercises and videos.
📌 Example: Smart tutoring systems like Carnegie Learning adapt to each student’s skill level.
3. Students
✔ Text-to-speech tools, screen readers, and speech recognition software help students with disabilities.
✔ Braille e-books and sign language translation apps improve accessibility.
📌 Example: The Kurzweil 3000 software helps students with dyslexia read and comprehend texts.
Global Efforts Toward Educational Equity 🌍
📌 UNESCO’s Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG4)
✔ “Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all.”
✔ Calls for free, quality primary and secondary education worldwide.
📌 Education for All (EFA) Initiative
✔ A global movement to provide universal primary education by reducing barriers for girls, refugees, and disabled students.
📌 The Right to Education Act (India)
✔ Guarantees free and compulsory education for children aged 6-14.
Conclusion: The Path to a Fair and Inclusive Education System
Achieving educational equity and inclusion is not just a goal but a necessity for building a just and progressive society. By addressing barriers such as poverty, disability, gender discrimination, and geographic challenges, we can ensure that every child receives a fair chance at success.
💬 What do you think is the biggest challenge in achieving educational equity? Share your thoughts below! 🎓🌎🔥